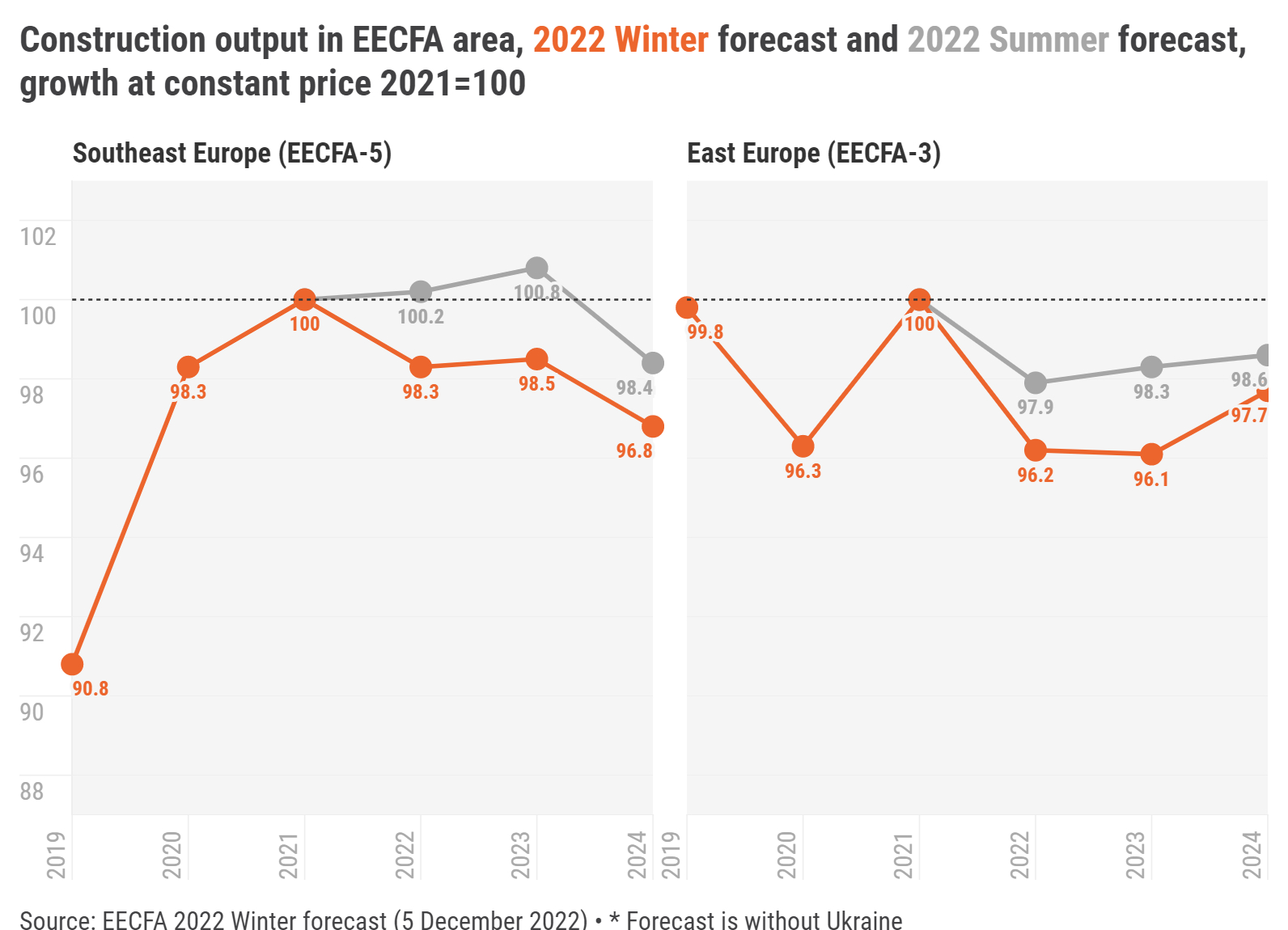
The EECFA 2022 Winter Construction Forecast Report has been released on 5 December. Yet another downward revision characterizes the forecast for both regions. Southeast Europe could see shrinkage on the horizon. This, however, comes after a great period of construction in between 2016 and 2021, so the market is foreseen to come down from a peak level. In this respect, the 3% decline until 2024 is no drama, in EECFA’s view. The drama is in East Europe where the peak was reached in 2018 and the market was around 10% below that peak level even before the Ukraine war began. Since then, EECFA has paused issuing forecasts in Ukraine and a status report has been prepared. Without Ukraine, the region is expected to reach its bottom in 2023.
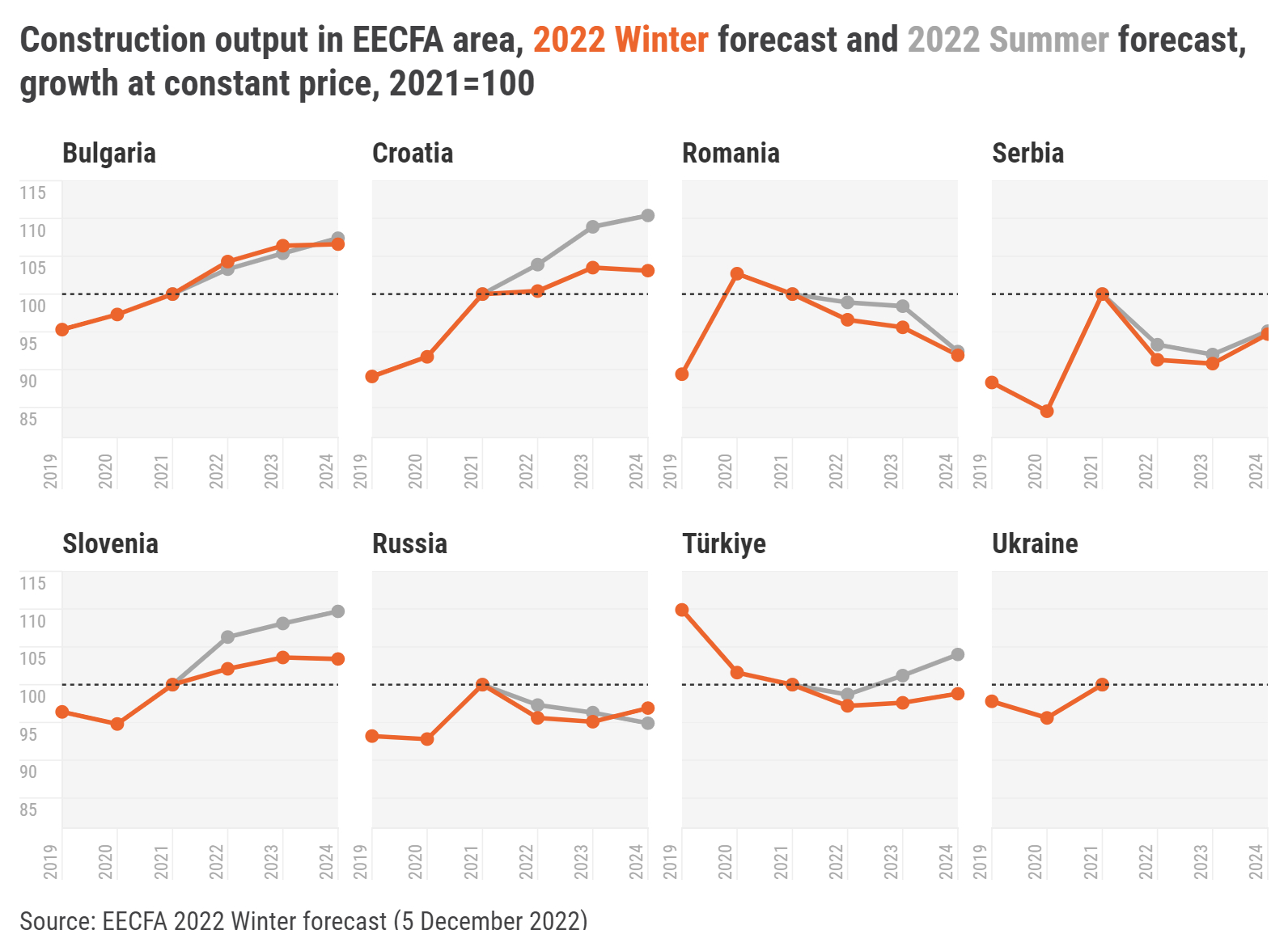
In Southeast Europe, almost all countries have been revised downward. Three out of them, however, could see expansion until 2024. The foreseen contraction in Romania and Serbia pulls down the region to negative. Romania is quite pessimistic; the market could shrink by almost 10% by 2024. Serbia is expected to witness a sizeable drop, too, before growth returns in 2024. As the region saw much construction in 2016-2021, the market will likely decline from the peak, making the 3% drop on the forecast horizon not-so-drastic.
Bulgaria:
Under the projected economic slowdown, construction will increasingly be affected by the ongoing political instability that is likely to undermine reforms within the Recovery and Resilience Plan, and delay implementation of the EU’s operational programmes.
Тotal construction output is estimated to have grown in 2022.
For 2023-2024 civil engineering is forecasted to increase at a more accelerated pace.
Croatia:
Residential construction output held up in 2022, impervious to war and disease. But it’s likely residential’s rapid growth will over time succumb to rising prices and a falling population.
Rail construction output will rise as more rail projects come online. Some new high-cost road projects may yet be undertaken for political reasons.
Energy prices will fuel building of oil/gas port facilities, pipelines and storage in 2022-2023, construction that the EU’s green-energy push may quench in favor of renewable energy and power grid projects.
Romania:
The Romanian construction market is set to shrink slightly in 2023 and 2024 as internal and external factors conspire to make building materials more costly.
Inflation-induced lower purchasing power and growing mortgage interest rates are making loans more expensive, and few people can afford to buy a home in cash.
On the one hand, Romania could benefit from the current global instability and attract more foreign investment to grow its economy. On the other, increased energy costs translate to higher operating and construction costs and discourage investment.
Serbia:
The challenging economic situation will undoubtedly have negative effects on construction outputs. But how negative is the question of external factors and the coming events.
The domestic market is strong, with high public and foreign investments, as well as record employment. The highest economic risk comes from inflation and the expected recession in the EU.
The current economic slowdown could deepen the contraction in case of a prolonged crisis.
Slovenia:
Slovenia has experienced expansion in construction output on the back of the strong overall economic growth.
However, risks for the future include high inflation, large construction cost increases, and overheating economic growth. And increased interest rates will depress residential output in the future.
Supply chain constraints might jeopardize the completion of large civil engineering projects.
In East Europe, 2022 could be the 4th consecutive year of drop in Türkiye, and no quick recovery is foreseen on the horizon. We have turned somewhat optimistic in Russia, but only from 2024 on. Without Ukraine, the region will likely hit bottom in 2023. The region reached its peak in 2018 and just before the war in Ukraine started, the market was around 10% below this 2018 level. Owing to the war, Uvecon, the Ukrainian member institute of EECFA, has prepared a status report for the second time instead of the forecast report.
Russia:
Direct and indirect effects of sanctions hammered the construction market that declined faster in 2022 than previously expected.
Forced acceleration of projects in transport and energy, in response to export and import structure changes due to sanctions, will spur growth in civil engineering.
Many targeted programs and national projects will support the construction sector throughout the forecast horizon.
Türkiye:
The construction industry has been trying to deal with high inflation that has led to 120% yearly rise in construction cost and 189% increase in housing prices.
There has been some deficit between produced and needed home numbers since 2000, augmented by the influx of refugees from Syria and neighbouring countries (3,920 million registered; unknown unregistered).
The low-cost housing project of the government as of September is expected to stop the current slump in the construction sector.
Ukraine:
Prospects for construction depend on the existing situation on the market as a result of the destruction of residential, non-residential and engineering infrastructure, and the end of hostilities with the possible economic recovery.
Total area of damaged or destroyed housing is 74.1 million sqm (7.3% of the total area of Ukraine’s housing stock), a number which, unfortunately, grows every day. Restoring the housing stock will become a key issue for Ukraine after the war ends.
Energy infrastructure remains the top priority for recovery, as nearly 40% of the energy system has been destroyed.
Source of data: EECFA Construction Forecast Report, 2022 Winter
If you would like to receive a sample report please use the following contact button or send an e-mail to sales@proidea.ro